New technology can be scary and confusing, but it does not have to be which is why we put together this quick guide on getting started with Microsoft Copilot.
It can be exciting and challenging to integrate Microsoft AI into your workflow. Artificial intelligence can boost Microsoft Office 365 productivity and streamline tasks with tools like Copilot. As you follow this guide, we’ll take you step-by-step through the steps to kickstart your AI journey with Copilot.
How to Enable Copilot in Your Favorite Office Apps
Copilot is available for Microsoft Office 365 apps, but if you can’t find the Copilot button, don’t worry – we’ve got you covered.
To enable Copilot, simply follow these steps:
- Make sure your Office applications are updated to the latest version. For seamless integration, this step is essential.
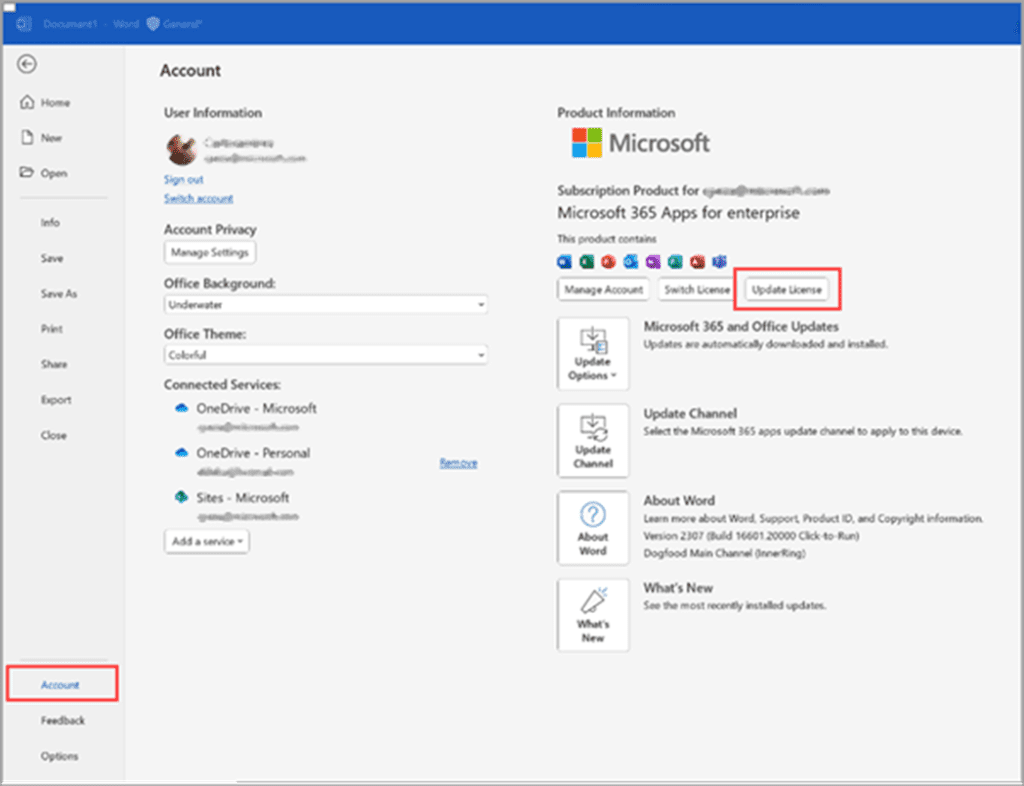
- To access account settings, open Word or Excel and select File > Account.
- You can update your license by going to your Account settings and selecting “Update License.”
- Enter your Office 365 credentials: You will be asked to provide your username and password.
- Your Office applications should now display the Copilot button prominently on the top left ribbon bar after the license update is complete.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Do you have a greyed-out Copilot button or are you having trouble accessing Copilot functionality?
Greyed out button? Here are some troubleshooting steps:
- A greyed-out Copilot button can be fixed easily.
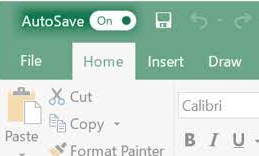
- Make sure AutoSave is enabled in Word or Excel. Make sure AutoSave is enabled by switching it on.
- For Copilot to work properly, files must be saved in SharePoint or OneDrive. You should save your files in one of these locations.
Can’t find the Copilot button in Outlook? Here’s what you need to do:
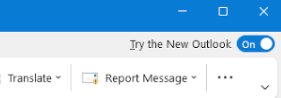
- Toggle the New Outlook switch: The New Outlook switch is located at the top right corner of your Outlook interface. You will need to wait a few minutes for the download and installation process to complete. You should expect some limitations and a different user experience with the new Outlook, as it is still in beta.
Exploring Microsoft Copilot Capabilities
As soon as Copilot is enabled in your Office applications, you can explore its many features. Copilot enhances productivity by assisting with document creation and simplifying data analysis.
Microsoft Copilot Helpful Links and Resources
- Microsoft Copilot Webpage
- Data, Privacy, and Security for Microsoft Copilot for Microsoft 365
- How to build Microsoft Copilot prompts
- Microsoft 365 Copilot in Excel (Video)
- Microsoft 365 Copilot Adoption Guide
- Microsoft 365 Copilot Training
- Microsoft 365 Copilot Roadmap
- ChatGPT vs. Microsoft Copilot
365 IT SOLUTIONS is excited to assist you as you embark on your AI journey with Microsoft Office 365 Copilot. This journey promises to revolutionize the way you work, offering countless opportunities to enhance productivity and efficiency. By following this beginner’s guide and troubleshooting tips, you’ll be well-equipped to harness the power of AI and streamline your tasks effectively. Keep in mind that as you progress on your journey, there’s always more to discover and explore with Copilot.
Stay tuned for updates and enhancements, as we remain committed to supporting our clients in their AI endeavors.
Happy exploring!
365 iT SOLUTIONS offers dependable IT support services to businesses in Toronto, making them a valuable resource for your IT needs.
We Make IT Simple!



